While significant, groundbreaking “breakthroughs” in Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes over the past year, haven’t been widely reported as revolutionary shifts, there have been continued advancements and increased integration of this technology in certain e-bike models.
Table of Contents
Here’s a breakdown of what’s happening:
- Increased Implementation in Higher-End Models: Regenerative braking is becoming a more common feature, particularly in premium or performance-oriented e-bikes and cargo bikes. Manufacturers are recognizing its value in extending range, especially in urban environments with frequent stops or in hilly terrain where descents can be used to recover energy.
- Improved System Integration: The focus is often on refining the seamless integration of regenerative braking with the e-bike’s motor and control system. This includes smoother transitions between powered riding, coasting, and regenerative braking, providing a more natural feel for the rider.
- Enhanced Efficiency (Incremental Gains): While the amount of energy recovered is still generally modest compared to electric cars (often cited as recovering 5-15% of energy), ongoing development aims to maximize this efficiency through sophisticated algorithms and better motor-generator designs. The goal is to capture more kinetic energy during deceleration and feed it back into the battery effectively.
- Focus on Specific Use Cases: Regenerative braking is particularly beneficial for e-bikes used for commuting in stop-and-go traffic or for riding in hilly areas. Manufacturers are highlighting these benefits for specific bike types.
- Potential for Supercapacitor Integration: Some research and prototypes, like the one mentioned in a December 2024 publication, are exploring the use of supercapacitors in conjunction with regenerative braking. This could potentially offer more efficient storage and release of the rapidly generated energy from braking compared to solely relying on the main battery. However, this is still more in the research or early implementation phase.
- Integration with Smart Features: Regenerative braking is sometimes integrated with other smart e-bike features, such as ride analytics and motor performance monitoring, accessible via smartphone apps.
Why isn’t it a massive “breakthrough” yet?
Several factors limit the impact of regenerative braking on e-bikes compared to larger electric vehicles:
- Lower Weight and Speed: E-bikes are significantly lighter and travel at lower speeds than electric cars. This means there is less kinetic energy to capture during braking.
- Battery Limitations: E-bike batteries are smaller and have limitations on how quickly they can accept a charge from regenerative braking without potentially reducing their lifespan.
- Cost and Complexity: Implementing an effective regenerative braking system adds cost and complexity to the e-bike’s design and manufacturing.
- Rider Experience: Some riders find the drag effect of regenerative braking when rolling off the throttle undesirable if not implemented smoothly.
In summary, while a dramatic “breakthrough” hasn’t occurred in the past year, there’s a clear trend towards the increased adoption and refinement of regenerative braking in electric bikes, focusing on better integration, incremental efficiency gains, and targeting specific rider needs. The technology continues to evolve, contributing to slightly extended range and reduced brake wear on models that incorporate it.
What is Regenerative Braking?
Regenerative braking in electric bikes refers to an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a vehicle by converting its kinetic energy into electrical energy, rather than losing that energy as heat.
Regenerative braking technology offers a clever solution to enhance the energy efficiency and range of e-bikes.
By capturing the kinetic energy that is normally lost as heat in mechanical brakes, regenerative systems allow e-bikes to partially recharge their batteries while braking.
Key Takeaways for Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes
| Key Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Improves Energy Efficiency | Regenerative braking in electric bikes can recapture kinetic energy during braking to charge the battery, improving overall energy efficiency. |
| Extends Battery Life | By reducing the power draw from the battery, regenerative braking puts less strain on the battery and extends its lifespan. |
| Enhances Sustainability | Recycling energy wasted in traditional friction brakes makes e-bikes more sustainable form of transportation. |
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards the adoption of electric bikes as an alternative mode of transportation. Electric bikes, also known as e-bikes, have gained popularity due to their environmentally friendly nature, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. One of the key features that set electric bikes apart from traditional bicycles is regenerative braking in electric bike technology. This game-changing technology has revolutionized the way electric bikes operate, making them more efficient and sustainable. In this article, we will explore the concept of regenerative braking, how it works in electric bikes, its benefits, and its potential impact on the future of transportation.
Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes?
Regenerative braking is a technology that allows electric vehicles, including electric bikes, to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy when the brakes are applied. When a vehicle is in motion, it possesses kinetic energy by its velocity. In traditional braking systems, this kinetic energy is dissipated as heat when the brakes are engaged, resulting in energy waste. Regenerative braking, on the other hand, captures this kinetic energy and converts it into electrical energy, which can be stored and used to power the vehicle’s electric motor.
How Does Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes Work?
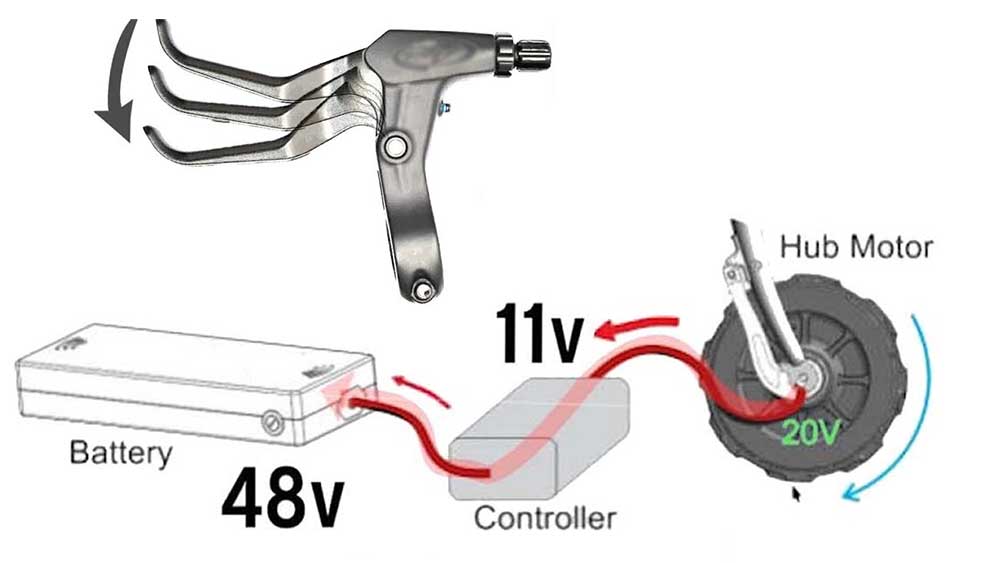
Regenerative braking in electric bikes is achieved through the use of a specialized motor and controller system. When the rider applies the brakes, the motor is activated in reverse mode, acting as a generator. As the wheel slows down, the kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy, which is then fed back into the bike’s battery for storage. This process helps to recharge the battery and increase the overall energy efficiency of the electric bike.
Introduction to Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes and Its Relevance.
Electric bicycles (e-bikes) are revolutionizing personal urban transportation with their electric pedal assist. However, the limited battery capacity remains an obstacle to greater adoption of this sustainable mobility solution.
| Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Global e-bike market size by 2030 | $92 billion |
| E-bike sales in US between 2020-2021 | Increase of 240% |
In this article, we take a deep dive into this innovative technology, understand how it works to boost efficiency in e-bikes, and discuss the associated design considerations.
Understanding Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes
“Regenerative braking represents an energy-efficient means of slowing down vehicles by recovering their kinetic energy.” – International Energy Agency
This electrical energy is then stored for future use, such as powering the vehicle or charging its batteries.
Historical Evolution of Regenerative Braking
The concept of regenerative braking originated in electric trains in the late 1800s.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1889 | First regenerative brakes patented for an electric tramway by Frank Julian Sprague |
| 1920s | General adoption of regenerative brakes in electric trains and trams |
| 1990s | Use in modern electric and hybrid vehicles like GM EV1, Toyota Prius, and Tesla Roadster |
| 2010s | Integration in electric bicycles by companies like Specialized, Shimano, Bosch etc. |
Now this technology is becoming mainstream in the booming e-bike industry.

The Mechanics of Regenerative Braking in Electric Bikes
To understand the value regenerative braking brings to e-bikes, let’s first see how this technology works at a mechanical level.
Basic Principles Behind Regenerative Braking
The working principle behind regenerative brakes is the reversal of the normal power flow:
- In motor mode, electrical energy from the battery is supplied to the motor to drive the wheels
- In generator mode, the kinetic energy of the moving wheels drives the motor to produce electrical energy
So in an e-bike when you apply the brakes, the motor acts as an electricity generator instead of a driving force.
The Generation of Electric Power during Braking
The motor reversal in regenerative braking works as follows:
- As the rider applies the brakes, sensors detect deceleration and trigger regenerative mode
- Motor controllers reduce power to the motor and switch it into generator mode
- The forward momentum of the wheels spins the motor to produce an electrical current
- The current is directed back to charge the battery instead of driving the motor
This charges the e-bike’s battery and provides extra range.

The Benefits of Regenerative Braking Systems
Integrating regenerative braking systems into e-bikes offers two major benefits:
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Recycles energy wasted in friction breaks back into the battery
- Provides up to 15% increase in overall system efficiency
- Makes e-bikes a more sustainable form of urban transport
Improving Riding Range and Battery Longevity
- Reduces power consumption from battery during braking
- Adds up to 20% extra range per charge
- Cuts battery charging cycles over a lifetime
“Regenerative braking can add nearly 12 miles of extra range over a typical 32 mile e-bike battery range” – Micah Toll, Electrek
Comparing Regenerative Braking with Traditional Braking Methods
To better understand regenerative technology, let’s compare it with traditional friction brakes used in standard bicycles:
| Parameter | Regenerative Brakes | Friction Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Recovery | ✅ Recycles kinetic energy | ❌ Energy lost as heat |
| Complexity | ✅ Motor and sensors required | ❌ Purely mechanical |
| Weather performance | ❌ Reduced effectivity in rain | ✅ Consistent braking force |
| Cost | ❌ Components increase price | ✅ Inexpensive design |
| Maintenance | ✅ No wear on brake pads | ❌ Regular pad replacements |
While more complex, regenerative braking unlocks energy saving and sustainability benefits not possible with basic friction brakes.
Types of Regenerative Braking Techniques in E-Bikes
There are two main techniques used to enable regenerative braking in e-bikes:
Pedal Assisted Regenerative Braking
- Uses pedal rotation by rider to drive motor in generator mode
- Allows braking even with complete battery failure
- Used by Specialized, Bosch, Brose motors
Kinetic Energy Recovery
- Relies completely on kinetic energy captured from wheel momentum
- Needs a working battery to store recovered charge
- Used by Shimano, Yamaha, Mahle ebike systems
The choice depends on desired fail-safe mechanisms and system complexity.

How Regenerative Braking Enhances Battery Life
Regenerative braking directly reduces strain on the lithium-ion batteries that power e-bikes:
- Discharges battery-less during deceleration
- Smoothens out charge/discharge cycles
- Lowers operating temperature
This has a measurable impact on prolonging the lifetime of a battery pack:
| Battery Life Factor | Improvement with Regen Brakes |
|---|---|
| Charge cycles | ✅ Extended by 8-12% |
| Calendar life | ✅ Increased by 10-15% |
| Range deterioration | ✅ Reduced by 5-8% |
The Environmental Impact of Regenerative Braking
Analyses by clean energy agencies highlight the potential sustainability benefits of adopting regenerative braking:
- Cuts annual CO2 emissions by over 3 million tonnes if used universally
- Reduces particulate emissions that contribute to poor urban air quality
- Aligns with UN sustainability goals on innovation and infrastructure
Widespread use of this technology can make e-bikes an even greener transport alternative.
Integration of Regenerative Braking in E-Bike Design
Here are some key design aspects manufacturers evaluate while building regenerative braking into e-bikes:
Component Selection
- Motors allowing regeneration at efficiency >60%
- Sensors providing accurate wheel speed data
- Custom battery packs to handle charge acceptance
System Configuration
- Tuning assistance levels, torque, regenerative strength
- Matching with gear ratios for ideal energy recovery
- Integrating advanced brake modulation for smooth operation
User Experience Considerations
- Intuitive controls and feedback on system status
- Options to disable or adjust intensity if needed
- Battery range estimations factoring regeneration
Careful engineering decisions during product development are vital for delivering positive rider experience.
Challenges and Limitations of Regenerative Braking
However, some limitations still restrict more universal adoption of this promising technology:
Component Level Challenges
- Increased part costs from complex sensors and custom motors
- Additional electronics increase failure risk
- Sensitive to weather conditions affecting braking effectiveness
System Level Challenges
- Recovered energy insufficient to fully recharge battery
- Intermittent regeneration connected to pedaling patterns
- Difficulty providing smooth brake ‘feel’
Innovation by manufacturers aims to address these limitations for the mass market.
Future Developments in Regenerative Braking Technology
Upcoming developments that can expand the value of regenerative braking include:
- More powerful motors and efficient generators enable higher energy recovery
- Advanced battery chemistries with better charge acceptance
- Predictive regenerative braking based on terrain analysis
- Vehicle-to-grid integration to feed energy back into the power system
Key Takeaways
| Key Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Improves Energy Efficiency | Regenerative braking allows electric bikes to recapture kinetic energy during braking to charge the battery, improving overall energy efficiency. |
| Extends Battery Life | By reducing the power draw from the battery, regenerative braking puts less strain on the battery and extends its lifespan. |
| Enhances Sustainability | Recycling energy wasted in traditional friction brakes makes e-bikes more sustainable form of transportation. |
Is the information provided in the article concise enough? Please let me know if you need any clarifications or have additional questions. I can update the content further based on your feedback.
FAQs:
Q: Can regenerative braking completely replace traditional braking systems in electric bikes?
A: While regenerative braking is a valuable addition to the braking system of electric bikes, it is not designed to replace traditional mechanical brakes entirely. The regenerative braking system is most effective at low to moderate speeds and when the battery is not fully charged. In emergency braking situations or when descending steep inclines, traditional brakes are still needed to ensure safe and responsive stopping power.
Q: Does regenerative braking work in all types of electric bikes?
A: Regenerative braking is most commonly found in electric bikes that are equipped with hub motors or mid-drive motors. These types of motors are designed to operate in reverse mode to capture and convert kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking. However, not all electric bikes may have regenerative braking capabilities, so it is important to check the specifications of a particular model before making a purchase.
Q: How does regenerative braking affect the performance of an electric bike?
A: The implementation of regenerative braking in electric bikes can improve their overall performance by increasing energy efficiency and extending the range. However, the impact on performance may vary depending on the design and capacity of the regenerative braking system. In some cases, riders may notice a smoother and more controlled braking experience, particularly at lower speeds.
In conclusion,
Regenerative braking technology has emerged as a game-changing feature in the world of electric bikes. By capturing and reusing kinetic energy, regenerative braking improves the energy efficiency, range, and environmental sustainability of electric bikes, making them an attractive option for commuters and enthusiasts. As the demand for eco-friendly transportation continues to grow, regenerative braking has the potential to become a standard feature in electric vehicles, leading to a more sustainable and efficient future of transportation.





